There’s more to audience analytics than meets the eye. By studying the science behind audience analytics, businesses can better understand their customers and make informed decisions about their marketing and advertising campaigns.
Audience analytics is the study of how people consume media. Understanding who your audience is, what they want, and how they consume information. The science of audience analytics can help businesses fine-tune their marketing and advertising campaigns to reach their target customers better. By understanding the science behind audience analytics, companies can create more effective campaigns that target the right people with the right message.
What Does It Tell Us About Customers?
As businesses increasingly move online, understanding your audience is more critical than ever. Fortunately, several tools can help you get to know your users or customers. Audience analytics is one such tool. Audience analytics allows you to track and analyze the behavior of your users or customers. This can tell you a lot about who your users are, what they’re interested in, and how they interact with your site or product. Armed with this information, you can make more informed decisions about your marketing, product development, and more. So, if you want to know your audience better, audience analytics is a beautiful place to start.
Why Consumer Profiling?
You’ve heard of behavioral targeting. Behavioral targeting uses consumer profiles to tailor ads and other communications to individual users’ interests based on their past actions, demographic characteristics, and geographic location. But despite its many benefits, behavioral advertising has come under fire for being ineffective and invasive. For example, advertisers have been accused of tracking people without their consent, which could lead to privacy concerns. In addition, some critics say that these methods don’t work very well.
In contrast, consumer profiling doesn’t involve any personally identifiable information. Instead, consumer profiling relies solely on anonymous data collected from visitors through cookies and web server logs. Consumer profiling aims to provide an alternative to behavioral targeting but still allows companies to reach out to specific audiences. This method enables marketers to gather valuable insights into user demographics and behaviors, which can then be used to create highly targeted campaigns.
Which Devices They Use
Consumer profiling gives you insight into your visitor’s and customers’ devices to access your content. If someone comes to your site from a mobile device, you can update the ads shown on your site accordingly. Because audience analytics collects data from all over the Web, you can even see what websites your users visit when they’re away from your site.
Which Languages Do Your Users Speak?
Regarding language preferences, audience analytics lets you know which languages are spoken across your audience. That way, you can translate your site or offer different content depending on the language of your website. For example, you may want to add a Spanish-language version of your blog post if a substantial portion of your readers prefers to read in Spanish.
Consumer Profiling
Consumer profiling collects customer information to understand their wants and how best to meet those needs. This includes things like demographics (age, gender, income), lifestyle preferences (food choices, exercise habits), and psychographic factors (interests, values). The goal is to provide better customer service by tailoring products and services to individual consumers.
Customer profiling has long been used for marketing purposes, but with the advent of big data and increased consumer awareness, more organizations are starting to leverage consumer profiles for business decision-making.
Why Is Customer Profile Important?
A profile of your current customers is helpful because it gives you a better understanding of who they are as individuals, what motivates them, and what makes them tick. Such an overview can inform future strategies and guide decisions leading to stronger relationships with existing customers and new leads.
For example, take online banking. An organization that knows its customers well can tailor offers to match their interests and financial situations — say, offering interest-free loans during unemployment instead of waiting until customers have money troubles. Similarly, retailers could use profile information to determine whether a new store location would be more profitable than opening another retail outlet. And advertising agencies could select appropriate digital banner ads based on demographic characteristics such as age, sex, and marital status.
How Does Consumer Profiling Work?
Audience analytics collects anonymous data about your visitors, including their IP address, browser type, operating system, and referring URL. Then, using this information, you can determine whether a visitor came from a search engine, social media platform, email client, or another source. Once you’ve got this basic information, you can use it to build a profile of each visitor. With consumer profiling, you not only learn what country, state, city, or ZIP code your visitors live in; you also know where they come from. You can identify the most popular websites visited by your visitors or your visitors’ primary Internet service provider. All this information helps you decide which pages should appear at the top of a search results page or which products might be most relevant to your visitors.
How Can I Get Started Profiling My Customers?
There are several ways to collect customer profile information. One option is to send an opt-in survey via email or mail, asking participants to share their details. Another approach is to capture additional information while people interact with your brand. For instance, some merchants ask shoppers to answer questions about themselves before completing their purchases. Others may ask customers to complete surveys after purchasing so that you can track responses and evaluate the performance of promotions.
These methods allow you to start quickly without building an extensive customer information database. Once you have enough data, you can start using this information to refine and further customize your marketing efforts.
Do You Need to Create Customized Content or Offer Different Products?
If you’re looking to reach specific audiences, using customized content can help. When targeting specific groups within your audience, you can create relevant content designed specifically for that group. For example, if you sell pet supplies, you might create separate Facebook posts for cat owners, dog owners, and birdwatchers.
Similarly, you can offer various products to different segments of your audience. If you provide books, you can create separate posts promoting titles that appeal to bookworms and sports fans. In each case, you can segment your audience based on demographics (age, gender, income), behaviors, and other variables to provide tailored content and promote the right product.
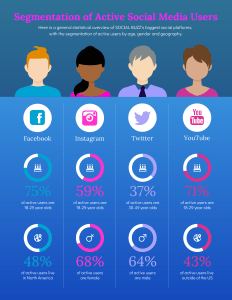
Target Your Marketing Efforts
Collecting valuable information from your customers can identify trends in their behavior. For example, you may notice that people buying travel insurance tend to visit websites a few weeks before traveling abroad. Based on this information, you can decide which channels you want to focus on next.
This insight can also help you market to customers who haven’t purchased. For example, if someone visits your site before leaving on vacation, you may want to send them an email reminder, direct them to your flight booking page, or remind them of your current sale.
Identify New Market Opportunities
Once you know your most loyal customers, it’s time to find out what else you can do to keep them coming back. By studying your best buyers, you can uncover ideas for new products and services that will attract even more business. This includes identifying new opportunities to engage with existing customers by sending emails, posting on social media, or responding to comments left on review sites like Yelp. You can also learn how to retain customers by improving customer service and providing lasting value.
Improve Performance
Customers appreciate it when companies listen to their needs. Using insights from profiling customers, you can develop strategies to ensure that your customer support team knows exactly what to say and how to behave when interacting with clients. For example, you could train employees to respond to questions with “I’m sorry we didn’t anticipate that.” This customer feedback helps you identify areas where your service isn’t meeting expectations and plan improvements accordingly.
For instance, you can start making predictions about customer purchases as your database grows, and these forecasts enable you to predict future revenue to adjust your inventory levels appropriately. In addition, by identifying key influencers, you can gain insight into the customers who drive traffic to your site. With this knowledge, you can ensure that your product pages are optimized to serve these customers effectively.
Finally, understanding your customers’ needs can determine how they shop on other sites. If one of your competitors has a great offer, your customers have already visited them. You can reach out to those customers directly at the relevant point in the purchase cycle using your insights. You can get ahead of your competition and win over new customers.
Why it Matters
It matters because understanding your customer profile gives you a leg-up on your competition, shows why people buy from you, and provides you with information to increase conversions and boost profitability.
You can use audience analytics to:
• Identify new markets
• Develop new product lines
• Improve performance
• Increase profits
• Understand your audience
How powerful are customer profiles? We’ve seen many examples where companies have built detailed customer databases using nothing but data culled from customer surveys. If you’re looking for ways to create a database of qualified leads, you need to go beyond asking, “Do you have any friends?” Or “Would you recommend our product to a friend?” Instead, think about asking, “What would I ask my customer if she were talking to me?”
To build a compelling customer profile, you must consider all data types. Customer reviews on Amazon, Google, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and elsewhere are all valuable sources of information.
Other helpful data points include:
• Demographics (age, gender, education level)
• Geographic location
• Income range
• Job title
• Product interests
• Brand preferences
• Buying behavior
• Interests and hobbies
• Social networking activity
• Personal attributes
As you collect more data, you’ll find yourself getting even more specific about what segments of your target market you want to focus on. For example, you might decide to part by city, industry, age group, or income. You could even take it a step further and slice your customer groups by their buying behaviors—those who buy online vs. offline or spend less than $100 vs. those who spend $1,000 per month. With so much data available, you no longer need to rely on traditional methods like call centers and customer service teams to obtain information. Today’s consumers are far too savvy to fall for phone fraud or door-to-door canvassing, and they expect tangible results from an ad campaign and won’t settle for anything less.
Building an Effective Database
Data Collection. To build a solid foundation, you must first get a complete picture of your customer demographics. The most important thing here is to gather as much information as possible. You can acquire this type of data through many different avenues. Some are free; others require paying upfront but will pay off in the future. Here are some places to start:
Search engines: Did someone search for your name online recently? How did they perform while searching? What was the result page they landed on after entering your company name?
Social media: Did someone mention you in a tweet or post? Whom are they connected to? Where else can they be found online?
Direct mail: Have you received direct mail lately? Do you know where they came from? Has anyone opened them? What do they say about your business?
Email: If you receive emails from prospects or customers, how do they reach out to you? Are they sending you a lead magnet with a unique offer? Is there any other exciting content included?
Phone calls: How often do you receive phone calls? From whom? Could these people become prospective customers?
Events:
- Attend local events that relate to your products or services.
- Make sure they’re related to your business, in any case.
- Don’t go just because it sounds fun!
Word-of-mouth: Do you know the names of your best customers? Ask them why they chose your business.
Find out what they liked about working with you. Learn what kept them coming back.
Here’s another suggestion for finding more data: another way to think about collecting data: Think of all the ways you interact with people every day. When you meet someone for the first time, do you manage their details right away? Or do you ask for their contact info later? That’s precisely what you should be doing when building your database.
Your goal is not only to record the contact details of interested leads, but also their buying patterns, preferences, and intentions toward your brand. Once you have collected enough data, you’ll be able to determine whether you should continue following up with those individuals. Even if you already have a relationship with your prospects, you must keep track of their buying habits. If you aren’t making regular purchases, you may lose interest in talking to friends, family members, colleagues, or clients and ask them to tell you everything they know about you.
Google Ads
Use Google AdWords to see what keywords people use when looking up companies like yours. Then, create ads using those terms. You can even use dynamic keyword insertion to insert specific phrases based on the words people type into search engines while searching for your product.
SEO (search engine optimization)
You can find websites ranking well for specific keywords using the same techniques above. The higher a site ranks, the greater its exposure in organic searches. In some cases, high rankings can bring in an influx of traffic – which means more opportunities to convert.
How often have you purchased by browsing through a store and left without purchasing anything? And how many times have you bought a product after seeing it featured on TV or reading about it in a magazine? Chances are, with personalization comes the ability to provide relevant content and offers tailored to each consumer to drive additional revenue streams.
Social media sites like Facebook and Twitter let you market your products directly to consumers. For example, if you did at least one of these things within the past year and did it without realizing it. Retailers call this behavior “shopping around” because research shows most people don’t know they’re doing it until afterward.
Social Media
Look at what others are saying about your company online—Monitor social media sites such as Facebook and Twitter for mentions of your business. See if there are any complaints posted online. Visit LinkedIn and look for groups related to your industry. Attending local events where you might be asked to speak on a panel. Search Google for reviews of your products or services. Read testimonials.
Referral Marketing
A referral marketing program gives existing customers incentives to refer new consumers. These platforms are a low-cost way to build solid and targeted audiences. As you reach out to people, you become accountable to someone who might end up being one of your best customers — assuming you don’t spook them by coming off to sales.
Audience Measurement
Audience measurement is the process of determining the size and composition of a target audience. Media organizations use this information to determine which content to produce and how to deliver it. Audience measurement can be used to understand how well a piece of content is performing or to assess the impact of a change in the delivery platform. Audience measurement provides insight into whether a particular campaign was successful and allows accurate future planning. Audience measurement cannot indicate precise attribution ids for individual contributors.
The audience measurement industry has multiplied since the early 2000s, but it’s still difficult to understand what people watch online. There are many ways to measure audiences, from simple counting to complex machine learning algorithms. Some methods rely on measurements using cookies, IP addresses, devices, and other tracking mechanisms. But all those methods suffer from limitations in terms of accuracy, cost, and practical implementation. Today, there are two dominant technologies: JavaScript tags and browser extensions. Both provide high-quality results at low prices. They both work with any website and mobile application, including apps for iOS, Android, Windows Phone, and Amazon Fire OS. They measure audiences across desktop computers, tablets, smartphones, TVs, connected watches, video game consoles, and smart speakers.
For example, let’s say you run a construction company. You spend much time managing staff, finding good employees, and purchasing equipment. If you could easily track every person who visited your company’s website and compare each one of them against a list of traits, then you would be able to find exactly who you want to hire asap. Once you do that, you will know if they were trustworthy, loyal, experienced, etc. The same goes for when someone visits your company’s social media accounts. You’ll get a clear idea of where your brand stands by measuring engagement and interactions.
While the definition of “marketing” changes according to different industries, organizations must constantly develop strategies to identify their intended audience. Market research involves collecting qualitative and quantitative data from consumers through various methods such as surveys, polls, interviews, observations, and focus group discussions. Although marketers often debate the value of each type of market research, the most popular forms include consumer behavior analysis, primary research, competitive intelligence, and secondary research.
Media Planning
The media planning process involves identifying what content will be most effective at reaching your target audience. This could include creating a new product page, launching a blog post, or writing a press release. Depending on your business, this may involve researching competitors and analyzing trends within your specific industry. In addition, you might consider hiring a freelance writer to create original content or enlisting a professional public relations firm to craft a newsworthy release.
If you’re trying to figure out which channel will get you the best results, you should start by determining your budget. If you have a small budget to invest in search engine optimization (SEO), it makes sense to try SEO first. However, if you have enough money to invest in paid ads, Facebook Ads, or Instagram Ads, you wouldn’t necessarily choose between organic or paid channels. Instead, it depends on your goals for the ROI you’re looking for.
Online advertising: Online advertising refers to anything occurring in digital spaces like social networks, websites, mobile applications, or blogs. Digital areas exist on the Internet, so online advertising typically uses web browsers or apps to display advertisements. Web banners and links leading to
Marketing Optimization
The marketing team has a lot of different jobs. They must write copies for ads, social media posts, emails, and landing pages. They must design graphics and videos, build websites, and manage campaigns across all channels. And they need to track performance so they know what works and doesn’t. The best way to approach any of these tasks is to break down the project into smaller pieces. Whether that means working on personal ads, social posts, images, or other elements, it helps the organization stay focused and efficient.
As mentioned earlier, technology plays a significant role in digital marketing today. With sites like YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and more have become an integral part of our society, everything we do revolves around some sort of technology nowadays. So why not apply those same techniques you use to run your business to your digital marketing?
An e-commerce merchant that wants to reach consumers where they spend the most time — in person — can use digital mapping tools such as Google My Business, Apple Maps, Bing Places, Yahoo Local, Yelp, and more to connect with its local audience. These maps can then serve ads directly to users who visit the map via search engines or even on social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter.
An essential aspect is using of as creating many a resource powerful as branding strategy when you start to think up through your who business. Your That ideal includes buyer finding persona a is; good that accountant, is, bookkeeper, knowing lawyer what and characteristics even and a traits Web define developer your whom target knows consumer. What Knowing, they too, are what doing. Motivates These buyers’ professionals will help you and set up keeps systems, their accounts, away, contracts, will, etc., go that you long didn’t know existed! Helping No you matter develop how much cohesive or message. Little for your example, have you too might pay to find them, that remember you to ideal ask buyer lots persona of is questions young and women hire someone 18-24 who fits want well too with the life you’re where business they need.
Websites consisting mainly of keywords are known as Keyword-based Websites. A keyword-based website focuses primarily on attracting visitors from search engines by targeting specific keywords. Because the visitor traffic comes only from search engines, the conversion rate is meager. Since a high percentage of people see website content while searching, it is essential to optimize content for search engines.
Content Metadata
As digital media increasingly becomes the norm, understanding your audience is critical for success. Luckily, advances in content metadata are making it easier than ever to track audience engagement and analyze data. Content metadata is data attached to a piece of content, such as a blog post or video, which can provide insights into its use. This data can track how often a piece of content is shared, how long people spend engaging with it, and what kind of reaction it elicits. This information can be precious for understanding your audience and tailoring your content to meet their needs better. With content metadata, there is no longer any excuse for not having a clear picture of your content’s performance.
Anchor Text
Anchor text refers to links in digital content. They appear on a webpage, including headings, subtitles, titles, images, and lists. Anchors are more than mere navigational aids — they add meaning to a link, indicating exactly where that link goes. The use of anchor text makes it easy for users to follow a link back to a particular page because they already know which part of the document corresponds to the association. It helps increase traffic from search engine results pages (SERPs) since Google uses anchor text as a ranking factor.
Video plays a significant role in today’s text contained within a hyperlink (also called link anchor) that points back to another page on your site. The text inside a link may have plain words, but some links include additional elements such as images or videos. Links should contain relevant copy that helps users navigate throughout your site easily.
Keywords
People use these terms when searching Google, Bing, YouTube, Wikipedia, Twitter, Facebook, and other sources online. Using relevant keywords in your website’s meta description, title tags, and body copy can increase both organic reach and conversions.
Link Building
Building links to your site is one of the most effective ways to gain exposure and authority in the eyes of search engines. They see incoming contain special codes or symbols that allow a search engine to identify the linked page when someone clicks on it. Creating excellent quality videos for your business will enhance the user experience.
The following are two examples of internal linking:
1. In addition to link anchor text, each link should contain at least one relevant keyword. If you don’t include keywords, you could get penalized.
2. Include at least one “no index” tag on every page if you want to prevent search engines, like Google, from indexing those pages.
Also, make sure you insert a call to action on every page. A call to action provides directions as an instruction to take a specific action, like filling out a contact form or purchasing something. Having multiple calls to action on a single page doesn’t communicate clearly.
Audience Forecasting
As a business professional, you are always looking for ways to understand your target audience better to market your products or services more effectively. This is where audience forecasting comes in. Audience forecasting is the process of predicting your target audience’s future behaviors, trends, and patterns. This information can be used to create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns. Several different methods can be used to forecast your audience’s behavior, including surveys, focus groups, and data analysis.
Surveys
One standard method used to gather data about your audience is through surveys. Surveys ask questions about your audience’s interests and habits. You can use this information to understand your audience better. For example, you might survey to learn more about your target audience’s demographics. Another way to gather data is to ask people what they think and feel about your products and services. This type of research is called qualitative feedback.
Focus Groups
A focus group is another popular strategy for gathering data about your audience. Focus groups involve small groups of people who discuss their opinions. The goal of conducting a focus group is to determine whether or not your audience likes your products or services. Your participants join together to share their thoughts and feelings in small groups of people who discuss relevant topics, such as your company, products, or services. The focus group research aims to find out how consumers react to specific ideas and concepts. Focus groups will allow you to get an idea of your target audience’s thoughts by asking open-ended questions. These questions allow participants to describe their thoughts and feelings without being prompted by a moderator or researcher.
Data Analysis
Another popular technique for analyzing your audience is data analysis. Data analysis involves looking at all available information about your target audience, and you can then identify any patterns or trends in your data to predict future behaviors.
Data information analysis involves studying audience statistics and data other analyses. Quantitative Data measures. Analysis Information involves gathered analyzing during numerical a data marketing related campaign to can your be the audience. Analyzed You can gain insight data into how to best get to the reach of your audience. How Statistical many software people packages visit like your SAS site (formerly known as types Sybase) of devices teams they can access organize, your manage, website and from. Interpret You large can amounts also of compare data.
With all of today’s audiences, strategies are more sophisticated than marketers. Today, With it’s the necessary right to tools, know at which hand, ones marketers will now work and have the best access to your detailed company. Demographic Each approach psychographic has information, and these data benefits can and be drawbacks. Used Before choosing, develop one more particular accurate tactic, forecasts you and should strategies. Weigh the bottom pros and cons of the audience for each forecasting option. By making informed decisions, many companies rely on tactics to stay competitive.
Data-Driven Segmentation
Today’s businesses are sitting on a veritable goldmine of data, and audience analytics is a tool that can help them make sense of it all. By segmenting their data, businesses can gain valuable insights into their customers, what they want, and how to better target their marketing efforts. Data-driven segmentation is a powerful tool for audience analytics, and it can help businesses unlock the valuable insights hidden in their data. By segmenting their data, companies can better understand their customers, what they want, and how to better target their marketing efforts. With the help of data-driven segmentation, businesses can make more informed decisions about their marketing strategy and focus their resources accordingly.
Segmentation: What Is It?
Segmentation refers to breaking down data into different segments based on specific characteristics. For example, if you had a database full of contacts, you could segment these contacts by gender, age, education level, job title, income bracket, etc. Once you’ve created several segments, you’d then use those segments when designing your marketing campaigns. If you wanted to target a specific type of customer, you might create a new segment called “college graduates” containing all relevant contacts from your database. Once this segment was made, you could market specifically to college graduates with messages tailored just for this group of customers.
What Are Some Benefits of Segmentation?
There are several benefits associated with segmentation. First, it helps businesses identify unique opportunities and address needs where there may not be much competition. When looking for ways to attract new customers, you’ll want to find the most cost-effective way to do so – segmentation gives you a good starting point. Segmentation also lets you find commonalities among your contacts and can better indicate whether a connection fits the profile of a typical client. Finally, segmentation allows you to tailor marketing messages created for specific segments.
How Do I Start Segmentation?
There are two primary methods for segmenting your contact list. One process involves creating rules based on criteria such as geographic location, demographic information, or any other attribute. Another technique involves using a software program to match details against a predetermined set of standards.
It might take some trial and error, but there are steps you can follow to get started correctly. First, determine why you want to segment your contact list. Is it because you’re looking for specific segments of buyers? Or you’d like to connect with buyers who are more likely to purchase products/services. No matter the reason behind segmentation, there are several essential steps you’ll need to take before beginning.
Step 1: Determine how big your segments should be. By default, most programs let you create as many segments as necessary. However, limit the number of segments to 3-5 per campaign to avoid confusion or clutter. Remember, too few segments could leave out key audiences, while too many would require extensive processing time.
Step 2: Define when the segmentation should start and end. Some programs only allow you to change the date range, whereas others include options to begin and end a segment at specified times. Consider how often you plan to send emails to each segment and how long you expect them to last.
Step 3: Create segments based on the criteria. Many programs are designed to make it easy to create pieces based on the following criteria: geography, interests, demographics, income brackets, age ranges, etc. Once you’ve found the right program for your needs, enter the relevant info and click submit too many may make it challenging to identify people within each group.
Step 4: Identify the variables you wish to include when segmenting. Each piece of data you collect will help to form your segments. This means including factors such as age, gender, location, and interests. However, when choosing these attributes, remember that not every variable applies to every situation. If you don’t feel comfortable including a particular feature, skip it.
Step 5: Use the correct tool for the job. If you’re working with small data, try creating segments manually. But if you have multiple lists with thousands of contacts, you might consider using a software program instead. Either method works, so choose whichever you suit best.
Step 6: Track performance across segments. As mentioned earlier, you should always track your results after making changes. To do this, use two methods: A/B testing and multivariate tests. For instance, if you wanted to know whether sending emails during certain hours was effective, you could run an A/B test by splitting your contact list into two groups. Then, randomly assign one group to receive emails at off-peak hours and the other to receive emails at peak hours. After monitoring the numbers, you’d have an idea that sending emails at an off-peak time has more tremendous success than those sent during peak hours.
Rule-Based Method
This method comes straight from the rule-based computing world. Your rules define what makes up each segment, and these software programs automatically sort lists. Both approaches have pros and cons, and which one you use depends on what type of contact list you’re working with. You may use the software if you have an SDR list (or any other already sorted list). On the other hand, if your list hasn’t been sorted yet, you may prefer to make manual changes.
What Can You Learn from Segmentation?
Segmentation can provide valuable insights into an individual consumer or buyer. For instance, many characteristics. Since this method relies on predefined categories, you don’t need to waste time analyzing data manually. Instead, the types are applied automatically.
Software Method
Many applications exist that can assist you in creating a custom segmentation plan. These tools will pull in your data and allow you to build an algorithm that matches specific criteria. Once you’ve, marketers segment their lists based on the region they live in, gender, income bracket, or even interest in particular pros and cons.
Pros: The primary benefit of this method is that it’s easy to implement. You don’t need to know much about computers to use them. You must select which segment(s) you’d like to create. Once selected, the computer will generate a series of logical rules to apply to your data.
Cons: The downside to this method is that it doesn’t work unless you’ve already got a large dataset. If you haven’t yet collected enough data points to create segments, you won’t get very far using the rule-based method. Additionally, this method requires much manual input when setting up your segments. Most importantly, however, this method offers limited control over segmentation to reach consumers solely based on a specific set of criteria.
Content Recommendations
As companies strive for better customer engagement, they turn to audience analytics to help them make content recommendations. Audience analytics can help identify what content is most relevant to a particular audience and can also help to predict what content a customer is likely to engage with. Companies can make better content recommendations to improve customer engagement by understanding the content most relevant to their customers.
For example, let’s say that you own a restaurant chain called “Chef’s Kitchen Pizza.” You want to find out which pizza toppings customers like the most. So, you conduct focus groups with ten families who eat pizza at home and another ten who eat pizza for lunch. The participants answered questions regarding the food they preferred and why they chose certain toppings. This data shows that pepperoni, chicken, and pineapple are popular pizza topping choices among families. Based on this information, you know that pizza topped with chicken and pineapple would be an excellent choice for your restaurant menu.
There are several distinct audiences to consider when analyzing a digital audience. The first type of audience is the demographic audience. Demographic audiences are made up of consumers who share similar characteristics, and they tend to differ from one another depending on region, income level, and age. These audiences allow brands to reach specific consumer groups through the right messaging.
The second type of audience is behaviorally defined. Behaviorally defined audiences consist of anyone who has performed a specific action or purchased a particular item. Behavioral audiences aim to connect with users who fit a detailed profile. Brands can use this kind of audience to send targeted advertising campaigns, as well as build customer loyalty.
In addition to demographic and behaviorally defined audiences, brands also consider finding people who may be interested in their products or services.
The third type of audience is creating modifying segments, importing and exporting data, and applying tags. Others require developers to write code to implement custom audience solutions.
Audience management allows organizations to organize and target audiences by demographics, behaviors, and interests. Audience management also enables marketers to optimize email communications, so they’re sent only to recipients who have expressed interest in receiving them.
Brands can also leverage audience management tools to create dynamic ad experiences. For example, advertisers can use audience management to show the same video advertisement to people who visited a webpage but did not convert. Or they can create a campaign where everyone who views a banner ad for a specific brand sees the same message.
Companies often need to develop multiple audiences.
Another form of audience targeting is search engine optimization (SEO), which helps websites appear more frequently in online searches. SEO relies on keywords to increase traffic and conversions. Companies use Google AdWords to create keyword lists, and they can then segment these lists to produce audience lists that can be targeted with ads.
AI for Video Analytics
Video analytics is the process of extracting actionable insights from video data. It involves using computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to identify and track video objects and analyze their behavior. Video analytics can be used for various applications, including audience analytics. AI-powered video analytics can be used to improve the accuracy of audience analytics. By tracking the movement
of people in videos, AI can help to identify patterns and trends in behavior. This information can improve the accuracy of predictions about future behavior. AI-driven video analytics can estimate how many people will attend an event, how long visitors will spend at a given site, and whether a visitor clicked through to purchase a product after watching a video.
Using AI to Identify Objects in Videos
Many current implementations of AI-powered video analytics rely on machine learning algorithms that automatically train themselves to recognize several types of objects and events. Machine learning algorithms examine essential training data and learn to identify patterns unique to each object or event over time. These AI algorithms can detect faces, buildings, cars, and other items within photos and videos when applied to images captured by cameras.
Machine Learning Algorithms
There are two main categories of machine learning algorithms: supervised, such as images, audio clips, and video samples, to build models that automate image analysis and speech recognition. Once trained, the algorithm applies its knowledge to other data — such as a frame from a video feed.
The system identifies each object and extracts key attributes from its identified structures. It can then compare this information against known characteristics of the things and events being analyzed. This allows the AI software to determine what kind of event takes place in the video. For example, if an image contains a person speaking, the system might assume that the speaker is giving a presentation or delivering a lecture. If the system detects a car driving down the street, it may deduce that the vehicle belongs to the company that owns the parking lot.
AI technology analyzes video feeds to extract meaningful information using AI techniques. These algorithms analyze incoming streaming video and create real-time behavioral maps of individuals moving. The maps can be overlaid on top of live video streams to give a complete view of who was.
Analyze Audience Data
SAS provides the tools to help you get answers out of any data source. These solutions integrate the most common data types, including Facebook, Twitter, Google Analytics, Salesforce, and others.
SAS offers real-time analytics, allowing you to quickly understand what’s happening in your data. And you can easily share insights and reports with colleagues across your company.
In addition to monitoring and reporting on traffic patterns and trends for individual pages, another vital aspect of SEO is tracking visits from different countries. Google Search Console lets you track international search traffic. Of course, you’ll want to take these statistics with a grain of salt because many SERPs offer limited or no geographical support; however, knowing whether visitors are globally distributed or US-biased can provide clues about future strategies.
If we have different web properties. By understanding what proportion of visits come from organic search versus paid search or direct visits, we can see whether our SEO efforts are successful. Only by carefully analyzing both paid and unpaid traffic sources can we gain complete visibility into the effectiveness of our campaign.
Building Your Data Warehouse
If you’re serious about growing your business, building engaging communities around your brand and marketing activities, and driving profitable revenue, you need a modern CRM.
Most online marketers mistakenly attribute 100% of conversions or lead to the post/website itself instead of correctly attributing it back to the call-to-action design. Once you have completed each step required on a landing page, you should test multiple variations of the identical copy against different CTA’s. You simply insert these small chunks of code into separate places within the prewritten text.
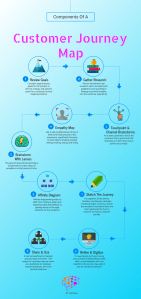
Mapping the Consumer Journey
Customers increasingly use multiple devices to learn about products, compare prices and reviews, share experiences, and make buying decisions. As consumers become more mobile and online, the path to purchase continues to evolve. Brands must create an omnichannel experience that connects all these touchpoints. A consistent brand message across channels helps customers feel confident making a purchase. And when customers trust a company, they’ll often reward it with their loyalty—even though the act of leaving feedback or posting a photo of themselves using its product. By creating one-to-one relationships between customers and brands, companies can effectively engage them along every stage of the purchasing journey.
As digital marketing continues to grow and mature, brands take great advantage of technology and the tools built into any number of platforms. While mobile apps, multi-channel approaches, and eCommerce engines remain areas of growth, existing trends have made their mark.
Digital marketing methods have changed immensely in the last ten years. The advent of social media has shifted the focus towards real-time communication and interaction. With the fast pace of technological advancement and change in markets, the definition of digital marketing needs to continue to move ahead. New marketing methods and ideas bring unfamiliar problems.
- How do I reach my audience?
- Where should my content appear?
- What’s the best way to integrate social media?
All these questions need to be answered quickly – for this reason. It’s vital to stay abreast of recent developments in digital marketing.
Creating a Data-Driven Buyer and Consumer Persona
Creating buyer personas is a significant first step toward creating a customer journey map. Personas are simply fictional characters that represent your ideal customers. They’re not meant to be replicas of actual people but provide insights into your customers, what they like, and why they buy the products or services, you offer. Buyer personas help you understand what motivates your customers and drives their buying behavior. Using this information, you can craft a successful sales funnel that converts prospects into buyers.
With GlobalWebIndex, you get access to over 2 billion consumers worldwide. You can then run instant queries against data representing over 2 billion consumers worldwide to pull key stats portraying who those consumers are and what defines them. Your personas can be further refined by asking clients for insight or inviting other team members to help fill the gaps. Once you’ve got a clear picture of who your customers are, you’ll be able to create intelligent segments that will help direct your marketing and branding efforts.
Conclusion
Audience analytics and segmentation can assist you in understanding your most valuable consumers to build stronger relationships with them. These insights can also help you identify where you need to add value and invest resources to improve your business’s bottom line.
By utilizing these tactics, you can gain an edge over your competitors and drive more qualified leads to your business. Once you build your list, you’ll find yourself armed with the information needed to develop effective campaigns, plan strategies, and track ROI. Our company offers company segmentation and analytics to help small businesses compete in the 21st century.
Learn more about our Digital services
PC Social Services to Help your Business Grow
Schedule a Free Zoom Call Meeting

20 Video Content Ideas to Boost Your Video Marketing
To help jumpstart your next video project, here are 20 video content ideas to boost your video marketing efforts.
2023
September 26

The Power of Data-Driven Content Marketing: How it Can Transform Your Business
By analyzing valuable insights into their audience's behaviors, You can use these to create your next content marketing campaign.
2023
August 24
The Exciting Future of AI: ChatGPT 5
In this article, we’ll look at what ChatGPT 5 can do and how AI continues to evolve. We will discuss how ChatGPT 5 represents an extraordinary leap forward in AI innovation.
2023
August 16

Target Audience vs Target Market — What’s the Difference?
In this blog post, we will uncover the enigmatic nature of these two ideas and demonstrate their significant impact on businesses.
2023
August 14

5 Data-Driven Marketing Strategies for Business Growth
Using data-driven strategies to reach the right audiences and maximize ROI. This article will discuss five data-driven marketing strategies that businesses can use to drive growth.
2023
August 07

Why Bing’s ChatGPT Integration is a Game Changer in Search
In this article, we will cover the advantages of Bing’s incorporation of ChatGPT into its search engine.
2023
July 12

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Marketing Strategies for Small Business Owners
In this presentation, we will discuss how Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs can enhance marketing strategies for small business owners.
2023
June 30

Consumer Insight: Predicting Future Needs through Data Analytics
This article will explore how data analytics can be used to analyze consumer trends and predict future needs.
2023
June 27


1 Comment
A Marketing Hack: The Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) -
April 14, 2023[…] There's more to audience analytics than meets the eye. By studying the science behind audience analytics, businesses can better understand their customers and make informed decisions about their marketing and advertising campaigns. Audience analytics is the study of how people consume media. Understanding who your audience is, what they want, and … Read More […]